
УДК 535.1
The theory of light developed simultaneously, as the movement of waves and corpuscles.
Isaac Newton suppose that light is a stream of particles. Christian Huygens believed that light is waves on the air. James Maxwell introduced the concept of electromagnetic waves. Heinrich Hertz received an electromagnetic wave in an experiment. Max Planck proved that light propagates and is absorbed in portions - quanta, which he called photons.
Such is the brief background of the fact that the photon was called the quantum of the electromagnetic wave.
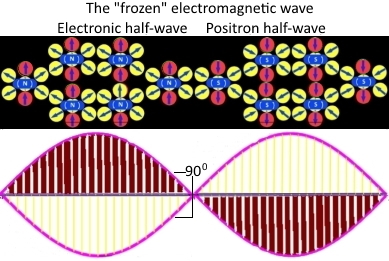
And it suited everyone until a half-educated philosopher arrived, who said: gentlemen, let the photon have neither electric nor magnetic charge, and therefore it cannot form the configuration of the electromagnetic wave, where the electric and magnetic components are perpendicular to each other and wave propagation vector. Moreover, this philosopher said that he made a discovery by inventing such a design of an electron and a positron that generates exactly the perpendiculars that are observed in electromagnetic waves.

And therefore, it is they — electrons and positrons — that are the quanta of the electromagnetic wave. And this fact is clearly proved by artificial electromagnetic waves, where in the receiving antennas the electromagnetic wave generates an electron-positron EMF.
EMF photons cannot form.
Thus, electromagnetic waves are waves of electrons and positrons, which emit photons through various types of radiation.
The fluxes of photons - this is light.
Thus, both directions of the study of light turned out to be correct.
And the final point in this study was put by a half-educated philosopher.
Light is an electromagnetic wave of electrons and positrons, the radiation of which turns light into streams of photons.
Thank God that God put these thoughts into the head of this philosopher.
Literature
1. Newton I. Philosophical problems of physics of the XX century. - M .: Nauka, 1991 .-- 205 p.
2. Huygens H. A treatise on light, which explains the reasons for what happens to it during reflection and refraction, in particular during the strange refraction of an Icelandic crystal. M.-L.: ONTI, 1935.
3. Maxwell, J. K. Selected works on the theory of electromagnetic fields. - M.: GITTL, 1952.
4. Herz G. On electrodynamic waves in the air and their reflection. // Ann. der Ph., B. 34, s. 609 ... 623. (Translated from German in the collection of "Classics of Physical Science"), M., Higher School, 1989.
5. Planck M. Selected Works (Moscow: Nauka, 1975).
Фундаментальная ошибка фундаментальной физики
Теория света развивалась одновременно, как движение волн и корпускул.
Исаак Ньютон полагал, что свет – это поток частиц. Христиан Гюйгенс считал, что свет - это волны в эфире. Джеймс Максвелл ввёл понятие электромагнитной волны. Генрих Герц получил электромагнитную волну в эксперименте. Макс Планк доказал, что свет распространяется и поглощается порциями – квантами, которы он назвал фотонами.
Такова краткая предыстория того факта, что фотон был назван квантом электромагнитной волны.
И всех это устраивало, пока не явился недоучившийся философ, который заявил: позвольте, господа, фотон не имеет, ни электрического, ни магнитного заряда, и потому он не может формировать конфигурацию электромагнитной волны, где электрическая и магнитная составляющие перпендикулярны друг к другу и к вектору распространения волны. Более того, этот философ заявил, что он сделал открытие, придумав такую конструкцию электрона и позитрона, которая генерирует в точности такие перпендикуляры, которые наблюдаются в электромагнитных волнах.
И поэтому именно они – электроны и позитроны – являются квантами электромагнитной волны. И этот факт со всей очевидностью доказывается искусственными электромагнитными волнами, где в приёмных антеннах электромагнитная волна генерирует электронно-позитронную ЭДС.
Фотоны ЭДС формировать не могут.
Таким образом, электромагнитные волны есть волны электронов и позитронов, которые посредством различных видов излучения излучают фотоны.
Потоки фотонов – это и есть свет.
Таким образом, оба направления исследования света оказались верными.
И завершающую точку в этом исследование поставил недоучившийся философ.
Свет – это электромагнитная волна электронов и позитронов, излучение которых превращает свет в потоки фотонов.
Слава Богу за то, что Бог вложил эти мысли в голову этого философа.
Используемая литература
1. Ньютон И. Философские проблемы физики XX века. - М.: Наука, 1991. - 205 с.
2. Гюйгенс Х. Трактат о свете, в котором объяснены причины того, что с ним происходит при отражении и преломлении, в частности при странном преломлении исландского кристалла. М.-Л.: ОНТИ, 1935.
3. Максвелл, Дж. К. Избранные сочинения по теории электромагнитного поля. — М.: ГИТТЛ, 1952.
4. Герц Г. Об электродинамических волнах в воздухе и их отражении. //Ann. der Ph., B. 34, s. 609...623. (Пер. с нем. в сб. «Классики Физической науки»), М.,Высшая школа, 1989.
5. Планк М. Избранные труды (М.: Наука, 1975)
Новые публикации: |
Популярные у читателей: |
Новинки из других стран: |
 |
Контакты редакции |
О проекте · Новости · Реклама |
 Молдавская цифровая библиотека © Все права защищены Молдавская цифровая библиотека © Все права защищены
2019-2024, LIBRARY.MD - составная часть международной библиотечной сети Либмонстр (открыть карту) Сохраняя наследие Молдовы |
 Россия
Россия
 Беларусь
Беларусь
 Украина
Украина
 Казахстан
Казахстан
 Молдова
Молдова
 Таджикистан
Таджикистан
 Эстония
Эстония
 Россия-2
Россия-2
 Беларусь-2
Беларусь-2

 США-Великобритания
США-Великобритания
 Швеция
Швеция
 Сербия
Сербия